CentOS 8 how to run Peernet as service: Step-by-step
This step-by-step assumes that you already have a complied Peernet binary in the /root folder of your CentOS 8 installation.
Create custom systemd service
Navigate to /etc/systemd/system
[root@ ~] # cd /etc/systemd/system [root@ system]#
Use editor of choice to create a new file called "peernet.service" (without quotes). In the following example, we are using nano.
[root@ system] # nano peernet.service
Copy/paste the following code in the newly created file.
[Unit] Description=Peernet binary service After=network.target [Service] WorkingDirectory=/root ExecStart=/root/Peernet Restart=always RestartSec=5 StandardOutput=syslog StandardError=syslog SyslogIdentifier=%n [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Exit nano, saving changes.
Ctrl + Z Y
Check directory for file
[root@ system] # ls
Reload systemctl to make new file visible
[root@ system] # sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Enable peernet.service (you should see second line if successful).
[root@ system] # sudo systemctl enable peernet.service Created symlink /etc/systemd/multi-user.target.wants/peernet.service -> /etc/systemd/system/peernet.service
Start peernet.service
[root@ system] # sudo systemctl start peernet.service
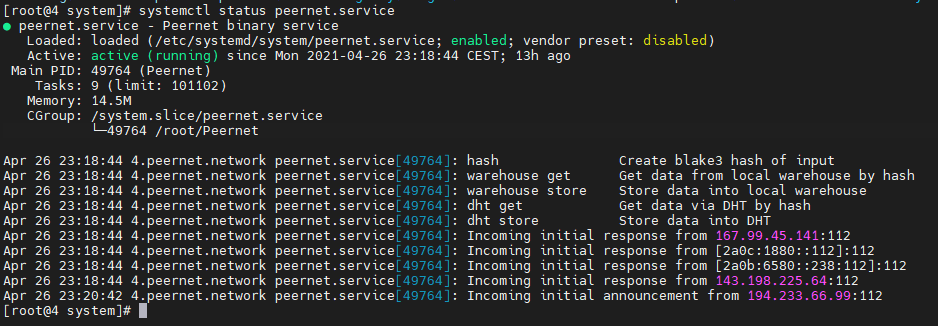
Check status of peernet.service
[root@ system] # sudo systemctl status peernet.service
Invoking ./Peernet while peernet.service is running
In order to start a working instance of ./Peernet, first stop the peernet.service. Otherwise the system will try to run two instances concurrently. From /root:
[root@ ~] # sudo systemctl stop Peernet [root@ ~] # ./Peernet
Howdy, Stranger!